
A Limited process will be just limited when it reaches the maximum allowed bandwidth, otherwise it will work as usual.Limited, Ignored, Dropped and Delayed processes are excluded when calculating bandwidth of High, Normal or Low priority processes.When there are no other processes with a higher priority using the network then processes with Low priorities will get all the bandwidth available.
Processes with a High priority will get more bandwidth than those with Normal or Low.Dropped - traffic that is dropped with a set drop rate.Ignored - traffic that is completely ignored.
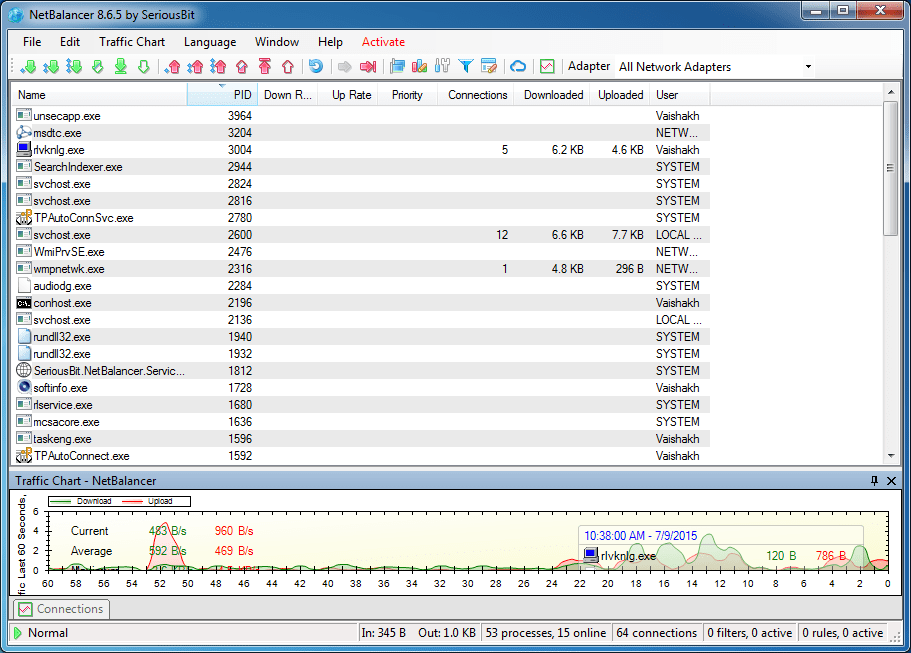
 Low priority traffic - traffic that has a network priority lower than both High and Normal. This means that if, for example, Firefox and Download Manager are downloading simultaneously some files right now, and Firefox has a High priority set for its traffic (while Download Manager has just a Normal priority) then Firefox will download the files much faster then Download Manager. High priority traffic - traffic that has the highest priority when sent or received by your computer. Limited traffic - traffic whose speed can't be higher than a set limit. Normal traffic - all the traffic that doesn't fall into the other 6 cathegories. This is a concept in NetBalancer that is used to delimit the network traffic in 7 main categories: It shows you the network traffic on your computer and helps you to set limits, priorities and rules for it. NetBalancer helps make sure that no one program dominates your bandwidth - just don't expect it to be instantly responsive.NetBalancer is a software application for monitoring and managing the network traffic of a computer or a group of computers. The point here is that the program can be slow to respond to bandwidth changes but it's certainly better than having to shutdown applications. In the initial stages of balancing, it can result in rather erratic bandwidths until the program has found the right medium (in which time, your needs might have changed anyway).
Low priority traffic - traffic that has a network priority lower than both High and Normal. This means that if, for example, Firefox and Download Manager are downloading simultaneously some files right now, and Firefox has a High priority set for its traffic (while Download Manager has just a Normal priority) then Firefox will download the files much faster then Download Manager. High priority traffic - traffic that has the highest priority when sent or received by your computer. Limited traffic - traffic whose speed can't be higher than a set limit. Normal traffic - all the traffic that doesn't fall into the other 6 cathegories. This is a concept in NetBalancer that is used to delimit the network traffic in 7 main categories: It shows you the network traffic on your computer and helps you to set limits, priorities and rules for it. NetBalancer helps make sure that no one program dominates your bandwidth - just don't expect it to be instantly responsive.NetBalancer is a software application for monitoring and managing the network traffic of a computer or a group of computers. The point here is that the program can be slow to respond to bandwidth changes but it's certainly better than having to shutdown applications. In the initial stages of balancing, it can result in rather erratic bandwidths until the program has found the right medium (in which time, your needs might have changed anyway). 
The problems begin when the balancing act is performed. The main difference between NetBalancer and other traffic monitoring software is that NetBalancer works with priorities, so applications with low priority won't be limited if other high priority applications don't use your network. Applications with a higher network priority will gain more traffic bandwidth than those with a lower one. NetBalancer can be used to set download and upload transfer rates by prioritizing which applications need them most.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
